center: [[6, 4]]
{'[1, 2]': 0, '[1, 4]': 0, '[1, 0]': 0, '[4, 2]': 0, '[4, 4]': 0, '[4, 0]': 0, '[1, 6]': 0, '[5, 6]': 0, '[9, 9]': 0, '[2, 7]': 0, '[3, 3]': 0, '[6, 4]': 0, '[2, 5]': 0, '[3, 5]': 0, '[4, 5]': 0, '[5, 5]': 0}
center: [[2, 7], [4, 5]]
{'[1, 2]': 1, '[1, 4]': 0, '[1, 0]': 1, '[4, 2]': 1, '[4, 4]': 1, '[4, 0]': 1, '[1, 6]': 0, '[5, 6]': 1, '[9, 9]': 1, '[2, 7]': 0, '[3, 3]': 1, '[6, 4]': 1, '[2, 5]': 0, '[3, 5]': 1, '[4, 5]': 1, '[5, 5]': 1}
center: [[3, 5], [5, 5], [3, 3]]
{'[1, 2]': 2, '[1, 4]': 0, '[1, 0]': 2, '[4, 2]': 2, '[4, 4]': 0, '[4, 0]': 2, '[1, 6]': 0, '[5, 6]': 1, '[9, 9]': 1, '[2, 7]': 0, '[3, 3]': 2, '[6, 4]': 1, '[2, 5]': 0, '[3, 5]': 0, '[4, 5]': 0, '[5, 5]': 1}
center: [[4, 2], [1, 0], [1, 4], [3, 5]]
{'[1, 2]': 1, '[1, 4]': 2, '[1, 0]': 1, '[4, 2]': 0, '[4, 4]': 3, '[4, 0]': 0, '[1, 6]': 2, '[5, 6]': 3, '[9, 9]': 3, '[2, 7]': 3, '[3, 3]': 0, '[6, 4]': 0, '[2, 5]': 3, '[3, 5]': 3, '[4, 5]': 3, '[5, 5]': 3}
center: [[5, 6], [4, 0], [1, 0], [3, 3], [6, 4]]
{'[1, 2]': 2, '[1, 4]': 3, '[1, 0]': 2, '[4, 2]': 3, '[4, 4]': 3, '[4, 0]': 1, '[1, 6]': 3, '[5, 6]': 0, '[9, 9]': 0, '[2, 7]': 0, '[3, 3]': 3, '[6, 4]': 4, '[2, 5]': 3, '[3, 5]': 3, '[4, 5]': 0, '[5, 5]': 0}
center: [[4, 5], [5, 6], [5, 5], [6, 4], [2, 5], [1, 0]]
{'[1, 2]': 5, '[1, 4]': 4, '[1, 0]': 5, '[4, 2]': 3, '[4, 4]': 0, '[4, 0]': 5, '[1, 6]': 4, '[5, 6]': 1, '[9, 9]': 1, '[2, 7]': 4, '[3, 3]': 0, '[6, 4]': 3, '[2, 5]': 4, '[3, 5]': 0, '[4, 5]': 0, '[5, 5]': 2}
center: [[1, 4], [3, 3], [4, 4], [6, 4], [2, 7], [1, 2], [3, 5]]
{'[1, 2]': 5, '[1, 4]': 0, '[1, 0]': 5, '[4, 2]': 1, '[4, 4]': 2, '[4, 0]': 1, '[1, 6]': 4, '[5, 6]': 2, '[9, 9]': 3, '[2, 7]': 4, '[3, 3]': 1, '[6, 4]': 3, '[2, 5]': 6, '[3, 5]': 6, '[4, 5]': 2, '[5, 5]': 2}
center: [[4, 0], [4, 5], [6, 4], [4, 4], [9, 9], [3, 3], [1, 4], [1, 2]]
{'[1, 2]': 7, '[1, 4]': 6, '[1, 0]': 7, '[4, 2]': 5, '[4, 4]': 3, '[4, 0]': 0, '[1, 6]': 6, '[5, 6]': 1, '[9, 9]': 4, '[2, 7]': 1, '[3, 3]': 5, '[6, 4]': 2, '[2, 5]': 6, '[3, 5]': 1, '[4, 5]': 1, '[5, 5]': 1}
center: [[3, 3], [9, 9], [5, 5], [3, 5], [1, 4], [4, 5], [4, 0], [1, 0], [6, 4]]
{'[1, 2]': 4, '[1, 4]': 4, '[1, 0]': 7, '[4, 2]': 0, '[4, 4]': 5, '[4, 0]': 6, '[1, 6]': 4, '[5, 6]': 2, '[9, 9]': 1, '[2, 7]': 3, '[3, 3]': 0, '[6, 4]': 8, '[2, 5]': 3, '[3, 5]': 3, '[4, 5]': 5, '[5, 5]': 2}
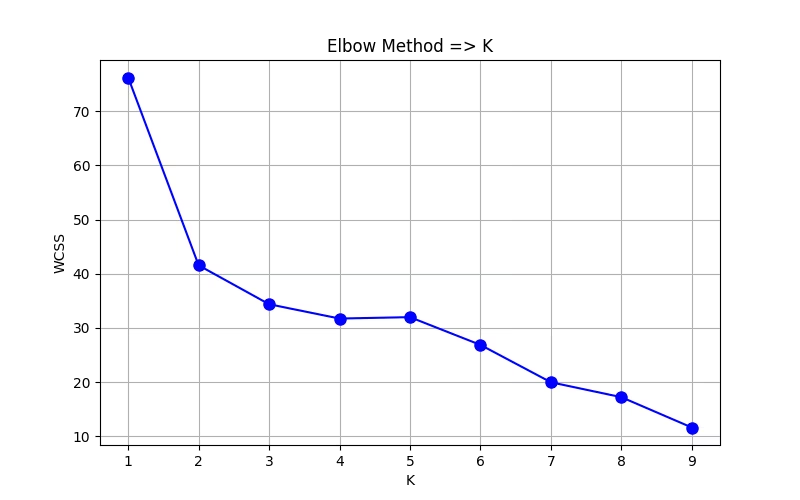
[58.638979289620025, 39.93955755931159, 28.611595782243192, 27.34009275541994, 25.482605577751237, 21.89292222699217, 19.471938219632754, 13.071067811865476, 10.650281539872886]
|